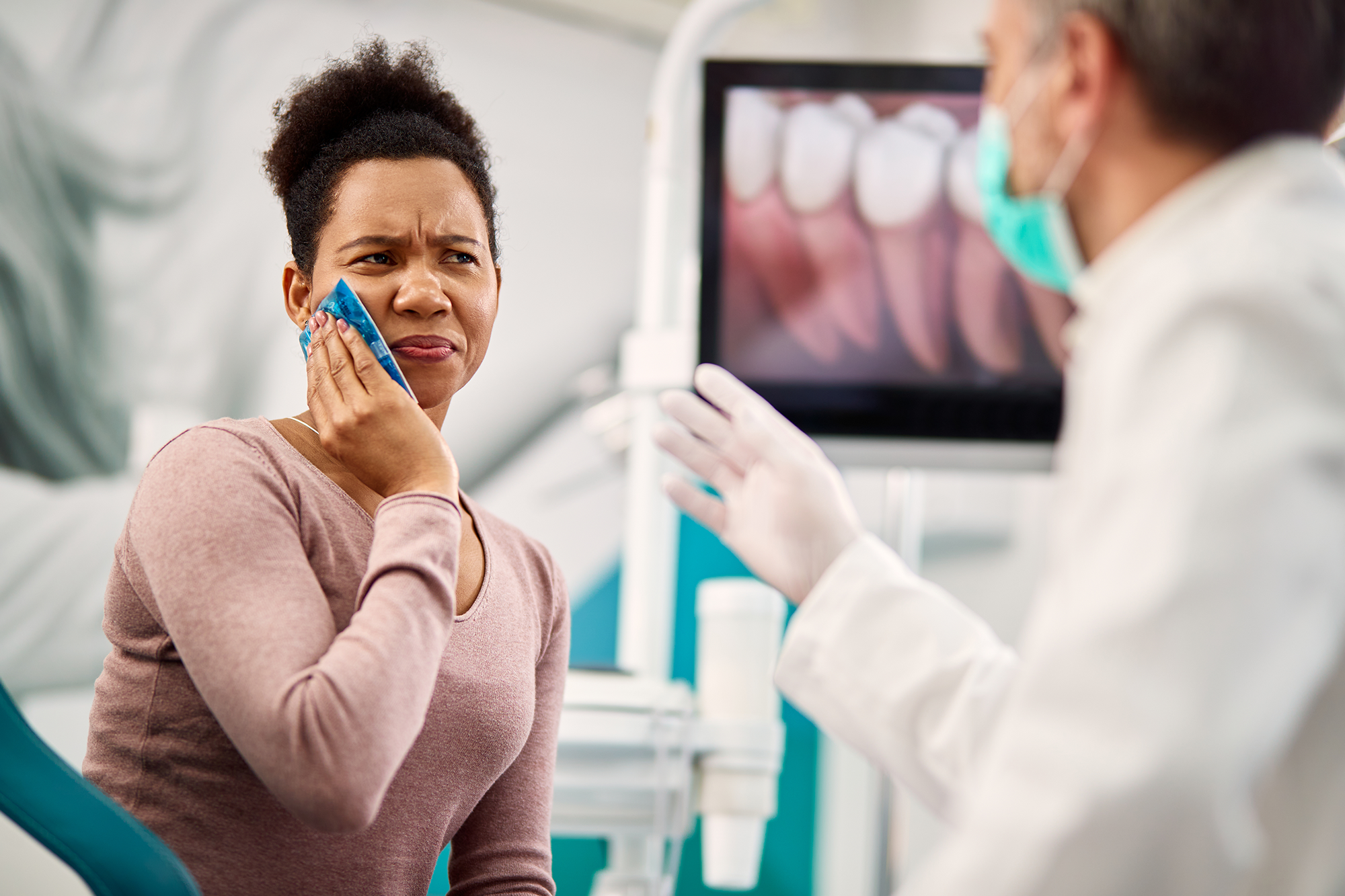
Maxillofacial trauma, including fractures, dislocations, or lacerations, often presents first to GPs or dentists.
Subtle fractures may not be visible on plain radiographs and can lead to long-term dysfunction if untreated.
Referral should be made when:
- There is swelling, asymmetry, occlusal change, or limited opening.
- History of impact with suspected fracture of jaw or zygomatic region.
- Chronic jaw pain, clicking, or locking persists despite conservative care.
Oral and maxillofacial surgeons assess with 3D imaging, stabilise fractures, and manage TMJ disorders with non-surgical or surgical options.
When to refer to AWOMS Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Any post-trauma with facial asymmetry, malocclusion, or persistent joint pain.