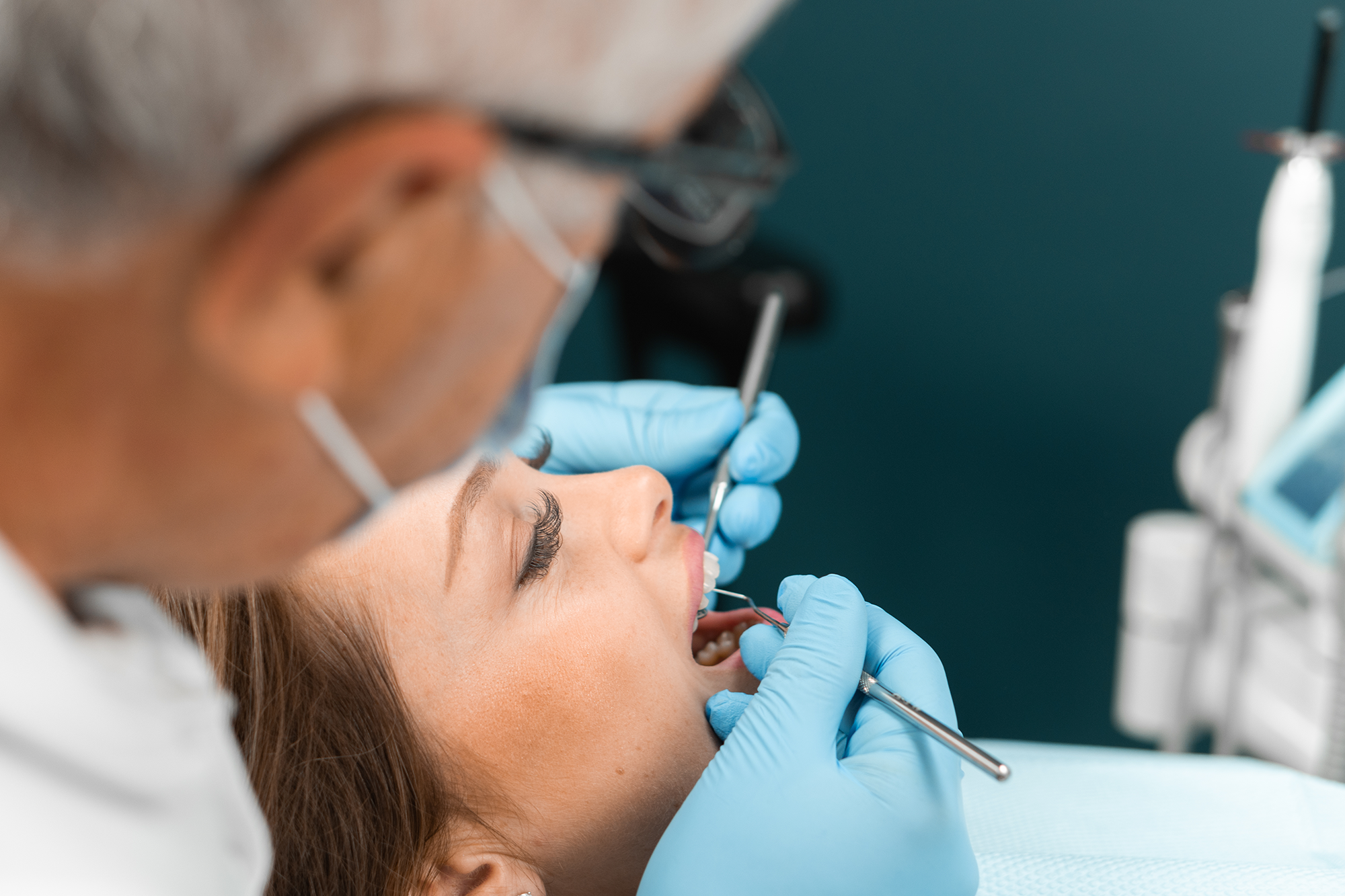
Retained roots or fractured root fragments are a common finding after difficult extractions and can lead to chronic infection, cyst formation, or sinus involvement if left untreated.
When fragments are close to vital structures such as the inferior alveolar nerve or maxillary sinus, surgical retrieval requires precision and careful planning.
Referral is appropriate when:
Radiographs show proximity of a retained root to the sinus floor or mandibular canal.
The patient reports persistent discomfort, swelling, or delayed healing.
There is a risk of sinus communication or nerve injury with further attempts.
In an oral and maxillofacial surgery setting, CBCT imaging is used to locate fragments accurately. Minimal access techniques, bone windows, or microsurgical instruments enable safe and complete removal while preserving surrounding bone and soft tissue.
When to refer to AWOMS Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: Any retained root near the sinus or inferior alveolar nerve, or when conventional removal poses a risk of complication or incomplete retrieval.